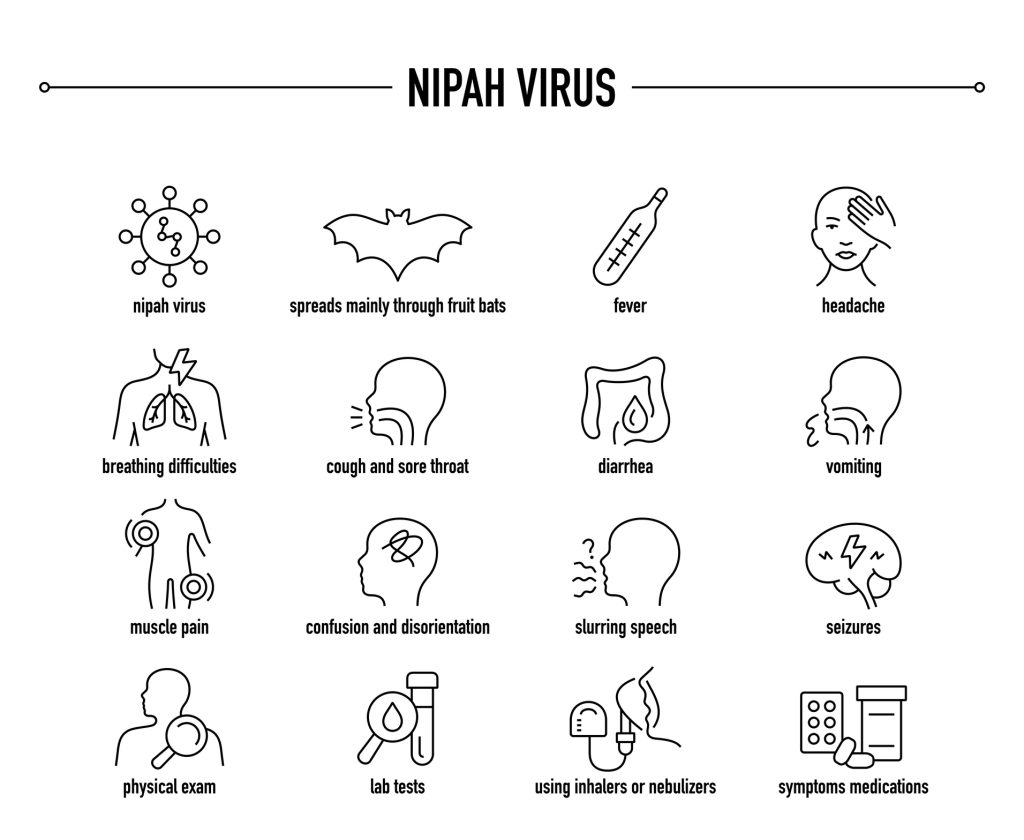
The emergence of the Nipah virus in Pakistan has raised serious public health concerns, highlighting critical risks associated with its spread. This zoonotic virus, primarily transmitted from bats to humans, poses significant challenges for healthcare systems. Here are seven critical health risks associated with the Nipah virus in Pakistan:
### 1. Human-to-Human Transmission
One of the most alarming risks of the Nipah virus is its ability to spread from person to person. Human-to-human transmission typically occurs through direct contact with infected fluids, such as saliva or secretions. This risk increases in densely populated areas and healthcare settings, where close contact with infected individuals can occur.
### 2. High Mortality Rate
Nipah virus infections can lead to severe respiratory illness and encephalitis, with a reported mortality rate ranging from 40% to 75%. The high fatality rate emphasizes the urgency of immediate medical intervention and public awareness campaigns to mitigate the impact of any potential outbreaks.
### 3. Limited Treatment Options
Currently, there is no specific antiviral treatment for Nipah virus infection. Supportive care is the primary approach, which may not be adequate for severe cases. The lack of effective treatment can lead to increased mortality rates, placing further strain on Pakistan’s healthcare resources.
### 4. Surveillance and Early Detection Challenges
Effective surveillance is critical in promptly identifying and containing outbreaks. Pakistan’s healthcare infrastructure may face challenges in implementing comprehensive surveillance strategies, hampering early detection and response efforts. Limited resources, particularly in rural areas, exacerbate this issue.
### 5. Impact on Agriculture
The Nipah virus is associated with fruit bats that can affect local agriculture, particularly crops like dates and bananas. An outbreak may not only impact public health but can also disrupt agricultural production and the economy, as farmers may resort to culling bats or crops to prevent infection.
### 6. Stigmatization of Affected Communities
The emergence of any infectious disease often leads to the stigmatization of affected individuals or communities. This social risk can deter individuals from seeking medical help or reporting symptoms, leading to further transmission of the virus. Education and community engagement are essential to combat misinformation.
### 7. Global Health Implications
Given the interconnectedness of today’s world, the emergence of Nipah virus in Pakistan poses not only local but also global health risks. International travel and trade mean that outbreaks can cross borders, necessitating collaboration between countries to share information and resources.
In conclusion, the Nipah virus presents multifaceted health risks for Pakistan, from high mortality rates and human-to-human transmission to economic repercussions. It is crucial for the government, healthcare systems, and communities to focus on preventive measures, enhance surveillance, and foster public understanding to effectively manage this emerging threat.
For more details and the full reference, visit the source link below:
Read the complete article here: https://brusselsmorning.com/pakistan-nipah-virus-health-alert/92844/